Spinal Cord Stimulators: a beam of hope in the treatment of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
Dr. Omar is an Anesthesiologist and Pain Management Physician who practices comprehensive Pain management in Tampa, Fl. Dr. Omar completed his Residency training at the prestigious Boston University followed by ACGME accredited Fellowship training in Interventional Pain Medicine at the distinguished program at University... more
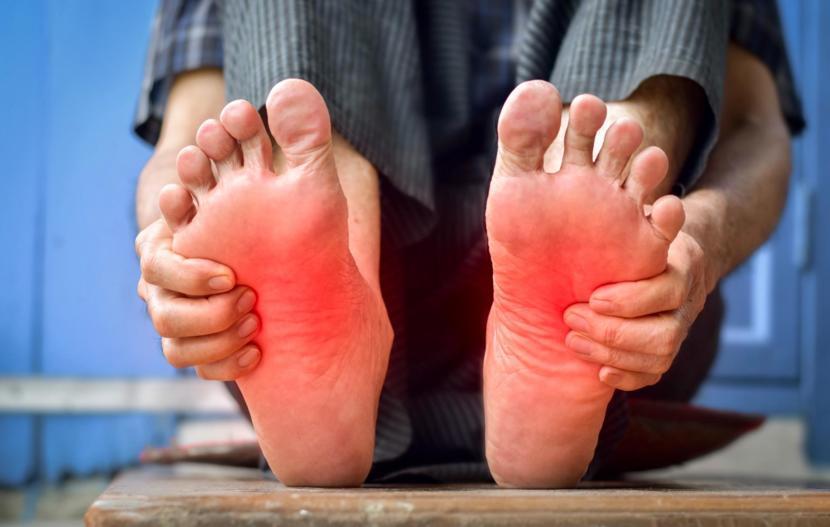
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (PDN) is a common complication of diabetes that can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands and feet. It can be a debilitating condition that affects the quality of life for many patients.
If you are suffering from PDN and are looking for relief, spinal cord stimulators may be a viable treatment option. Spinal cord stimulators are small, implantable devices that deliver electrical impulses to the spinal cord to block pain signals from reaching the brain.
Studies have shown that spinal cord stimulators can be an effective treatment for PDN. In a review of 12 clinical trials, spinal cord stimulators were found to significantly reduce pain and improve quality of life for patients with PDN (Lam, 2016). Another study found that spinal cord stimulators led to a reduction in pain of up to 50% in patients with PDN (Finnerup, 2015).
At our clinic, we have seen firsthand the positive impact spinal cord stimulators can have on the lives of patients with PDN. If you are interested in learning more about this treatment option and how it may be able to help you, I encourage you to schedule a consultation with an Interventional Pain Specialist that offers this therapy.
Mohammed Omar, M.D.
Aspire Pain Relief Institute
Tampa, FL
call (813) 296-5939 for an appointment
References:
- Finnerup, N. B., & Jensen, T. S. (2015). Spinal cord stimulation for neuropathic pain. The Lancet Neurology, 14(4), 414-423.
- Lam, T. K., & Kumar, K. (2016). Spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Medicine, 17(4), 647-657.









